In een stressvolle en snelle omgeving is het nuttig om bij het nemen van beslissingen meer dan eens op uw intuïtie te vertrouwen.
Maar weten wanneer je je moet toepassen intuïtief denken is lastig. Als u begrijpt wat het is en hoe u het kunt laten werken, kunt u goede beslissingen nemen met goede resultaten.
Duik erin voor meer inzichten👇
Inhoudsopgave
- Wat is intuïtief denken?
- Wat zijn de vier soorten intuïtief denken?
- Zijn intuïtieve gedachten goed of slecht?
- Tips om een meer intuïtieve denker te worden
- Tot slot
- Veelgestelde Vragen / FAQ
Meer tips voor het ontwikkelen van zachte vaardigheden
| Wat is het tegenovergestelde van intuïtief denken? | Contra-intuïtief |
| Wie heeft de term 'Intuïtief Denken' bedacht? | Henri Bergson |
| wanneer was?term 'Intuïtief denken' gevonden? | 1927 |

Op zoek naar een betere betrokkenheidstool?
Maak het nog leuker met de beste live polls, quizzen en spelletjes, allemaal beschikbaar op de presentaties van AhaSlides, klaar om te delen met uw publiek!
🚀 Meld u gratis aan☁️
Wat is intuïtief denken?

Stel je voor dat je een professionele honkballer bent die aan de thuisplaat staat. De pitcher draait zich om en gooit een fastball recht op je af. Je hebt een fractie van een seconde om te reageren – er is geen tijd om bewust na te denken!
Maar er gebeurt iets wonderbaarlijks: je lichaam weet wat het moet doen. Zonder enige logica zwaaien je handen in positie en knallen! Je krijgt een perfecte slag.
Waar kwam dat inzicht vandaan? Jouw intuïtie.
Diep van binnen herkende een deel van je hersenen subtiele signalen, zoals de bewegingen van de werper, de balbeweging, etc. en wist op basis van duizenden herhalingen tijdens trainingen en eerdere wedstrijden precies hoe je moest reageren.
Dat is intuïtief denken in actie. Het stelt ons in staat om vrijwel direct rijke ervaringen aan te boren en 'onderbuikbeslissingen' te nemen zonder enige bewuste logica.
Zoals hoe Cruise in Top Gun gewoon de juiste bewegingen voelt in luchtgevechten of hoe Neo de Matrix-code ziet zonder het te begrijpen.
Het mooiste is nog wel dat intuïtie niet alleen voor reacties is – het is ook een superkracht voor inzicht en creatie.
Die ‘aha!’-momenten van begrip of innovatieve oplossingen komen vaak uit onze intuïtie naar boven voordat de logica ze volledig kan verklaren.
Wat zijn de vier soorten intuïtief denken?
Intuïtief denken wordt over het algemeen onderverdeeld in vier soorten, elk met verschillende kenmerken. Welk type intuïtieve denker ben jij?🤔
Cognitieve intuïtie
Hierbij gaat het om het verkrijgen van inzicht in de patronen en gevolgtrekkingen die we onbewust hebben geleerd door ervaringen met cognitieve uitdagingen.
Het maakt snelle afstemming van schema's en oordelen mogelijk. Voorbeelden zijn onder meer het onmiddellijk herkennen van grammaticapatronen, het oplossen van complexe problemen, het intuïtief aanvoelen van het antwoord op een wiskundig probleem op basis van bekende patronen, of evaluaties van risico's/betrouwbaarheid.
Affectieve intuïtie

Ook wel onderbuikgevoelens genoemd. Dit type vertrouwt meer op emoties en gevoelens om intuïties te sturen.
Dingen kunnen goed voelen of ons een ongemakkelijk gevoel geven zonder dat we er bewust over nadenken. Het speelt een rol bij zaken als interpersoonlijke oordelen, het detecteren van bedrog en ethische/morele besluitvorming, waarbij emoties een rol spelen.
Analytische intuïtie

Ontwikkelt zich vanuit uitgebreid, deliberatief en automatisch leren gedurende jaren in een vaardigheid of domein.
Deskundigen kunnen complexe situaties intuïtief interpreteren en gepast reageren. Voorbeelden zijn onder meer meesterschakers, deskundige artsen en andere professionals met diepgaande ervaring in hun vakgebied.
Belichaamde intuïtie

Vertrouwt op spier-, proprioceptief en sensorisch leren.
Ontwikkelt door fysieke oefening en op beweging gebaseerde sociale ervaringen. Zaken als coördinatievaardigheden, evenwicht, het interpreteren van non-verbale emotionele/sociale signalen via gezichtsuitdrukking, lichaamstaal, enz. vallen in deze categorie.
Sommige bevatten ook:
- Sociale intuïtie – Verwijst naar het vermogen om intuïtief sociale dynamiek, normen en interacties te begrijpen zonder bewust te redeneren. Gebieden die het beïnvloedt, zijn onder andere het interpreteren van emoties, het voorspellen van gedrag, het onderscheiden van relaties en machtsstructuren, en het aanvoelen van groepsinvloeden/-dynamiek.
- Generatieve intuïtie – Nieuwe ideeën en innovaties opwekken of problemen op een nieuwe manier zien door verschillende soorten informatie intuïtief te synthetiseren. Voorbeelden hiervan zijn uitvindingen, innovatief ontwerp, baanbrekende wetenschappelijke theorieën en onverwachte perspectieven in de kunsten/geesteswetenschappen.
Alle vier de typen bieden snelle inzichten die mogelijk langzamer bewust toegankelijk zijn. En ze werken vaak op elkaar in: cognitieve patronen kunnen affectieve reacties oproepen die op de lange termijn van invloed zijn op ervaringsleren. Het effectief ontwikkelen van welke vorm van intuïtie dan ook is afhankelijk van voortdurende blootstelling aan nieuwe ervaringen en reflectief leren.
Zijn intuïtieve gedachten goed of slecht?
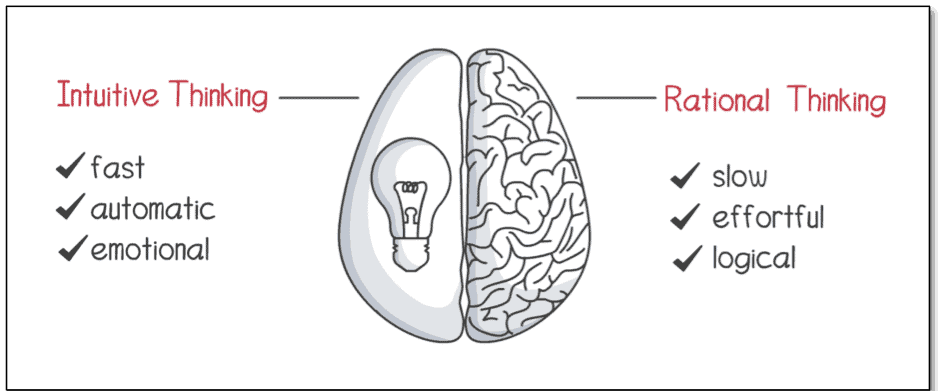
Intuïtief denken is een tweesnijdend zwaard. Het kan zeer nuttig zijn als expertise is opgebouwd door middel van uitgebreide ervaring, maar gevaarlijk als er op wordt vertrouwd bij beslissingen met hoge inzet die geen wetenschappelijke basis hebben.
Potentiële voordelen van intuïtief denken zijn onder meer:
- Snelheid – Intuïtie zorgt voor heel snelle besluitvorming wanneer de tijd beperkt is. Dit kan voordelig zijn.
- Inzichten op basis van ervaring – Intuïtie omvat de onbewuste lessen van ervaringen, die nuttige perspectieven kunnen bieden.
- Creativiteit – Intuïtie kan nieuwe verbindingen en innovatieve, out-of-the-box ideeën creëren.
- Eerste vermoedens – Intuïtieve onderbuikgevoelens kunnen dienen als startpunt voor verdere verkenning en validatie.
Potentiële nadelen van intuïtief denken zijn onder meer:
- Vooroordelen – Intuïtie is vatbaar voor cognitieve vooroordelen zoals ankergedrag, affectieve heuristiek en favoritisme binnen de groep, die oordelen vertroebelen.
- Ongeldige patronen – Intuïtieve patronen kunnen gebaseerd zijn op verouderde, onjuiste of eenmalige ervaringen uit het verleden, in plaats van op gedegen bewijs.
- Rechtvaardiging – Er bestaat een instinct om intuïtieve gedachten te rechtvaardigen in plaats van onpartijdig de juistheid ervan te onderzoeken.
- Holisme boven detail – Intuïtie richt zich op bredere thema’s in plaats van het zorgvuldig analyseren van belangrijke subtiliteiten.
- Zelfgenoegzaamheid – Intuïtie kan grondig, weloverwogen redeneren ontmoedigen en in plaats daarvan op gevoel afgaan.
Tips om een meer intuïtieve denker te worden

Hier zijn enkele tips om een meer intuïtieve denker te worden. Na verloop van tijd versterken deze strategieën uw intuïtieve denken door middel van diverse, reflectieve blootstelling en flexibel denken:
- Doe uitgebreide praktijkervaring op in je vakgebied. Intuïtie komt voort uit het onbewust herkennen van patronen in de dingen waaraan je bent blootgesteld. Daag jezelf voortdurend uit.
- Beoefen mindfulness en zelfbewustzijn. Let op je onderbuikgevoelens en ingevingen zonder te oordelen. Na verloop van tijd zul je leren meer op je intuïtie te vertrouwen.
- Moedig divergent denken aan. Maak associaties tussen niet-gerelateerde concepten. Brainstorm breed. Intuïtie combineert ideeën op nieuwe manieren.
- Neem pauzes tijdens het oplossen van problemen. Door incubatie kunnen intuïties uit uw onderbewustzijn naar boven komen. Ga wandelen en laat je gedachten afdwalen.
- Ontwikkel metacognitie. Analyseer eerdere intuïties – wat klopte en waarom? Bouw zelfkennis op over je intuïtieve sterke punten.
- Besteed aandacht aan je dromen/dagdromen. Deze kunnen intuïtieve inzichten bieden die buiten de logische normen vallen.
- Bestudeer domeinen die verschillen van jouw expertise. Nieuwe informatie voedt uw intuïtieve associaties en probleemoplossende invalshoeken.
- Vermijd het ontslag van een onderbuikreactie. Geef ingevingen een kans door ze verder te onderzoeken voordat je ze weggooit.
Tot slot
Intuïtief denken is gebaseerd op snelle, onbewuste patroonherkenning, emoties en ervaring in plaats van stapsgewijs redeneren. Met oefening kunnen we onze intuïtie trainen om bijna als een zesde zintuig te werken, waardoor we in elke situatie geweldige probleemoplossers worden.
Veelgestelde Vragen / FAQ
Wat doen intuïtieve denkers?
Intuïtieve denkers vertrouwen primair op hun onderbuikgevoelens, impliciete patronen die door ervaring worden herkend en het vermogen om intuïtief uiteenlopende ideeën met elkaar te verbinden, in plaats van op strikte logische analyses bij het benaderen van problemen, het nemen van beslissingen en het uiten van zichzelf.
Wat is een voorbeeld van intuïtief denken?
Een voorbeeld dat intuïtief denken illustreert, is: een schaakgrootmeester die direct de beste volgende zet herkent, zonder bewust alle mogelijkheden te analyseren. Hun intuïtie is gebaseerd op uitgebreide ervaring, of een ervaren arts die de oorzaak van onbekende symptomen bij een patiënt ontdekt op basis van subtiele signalen en het "gevoel" dat er iets niet klopt, zelfs als de testresultaten dat nog niet verklaren.
Is het beter om logisch of intuïtief te zijn?
Er is geen eenvoudig antwoord op de vraag of het inherent beter is om logisch of intuïtief te zijn – beide hebben hun sterke en zwakke punten. Het idee wordt over het algemeen beschouwd als een balans tussen beide benaderingen.








