在組織成功的動態格局中,關鍵在於持續改善的方法。無論您是領導一個小團隊,還是管理大型企業,追求卓越的精神永無止境。在本篇部落格文章中,我們將探討 5 種持續改善方法和 8 種持續改善工具,以揭開促進組織創新、提高效率和持久成功的秘訣。
目錄
什麼是持續改進?
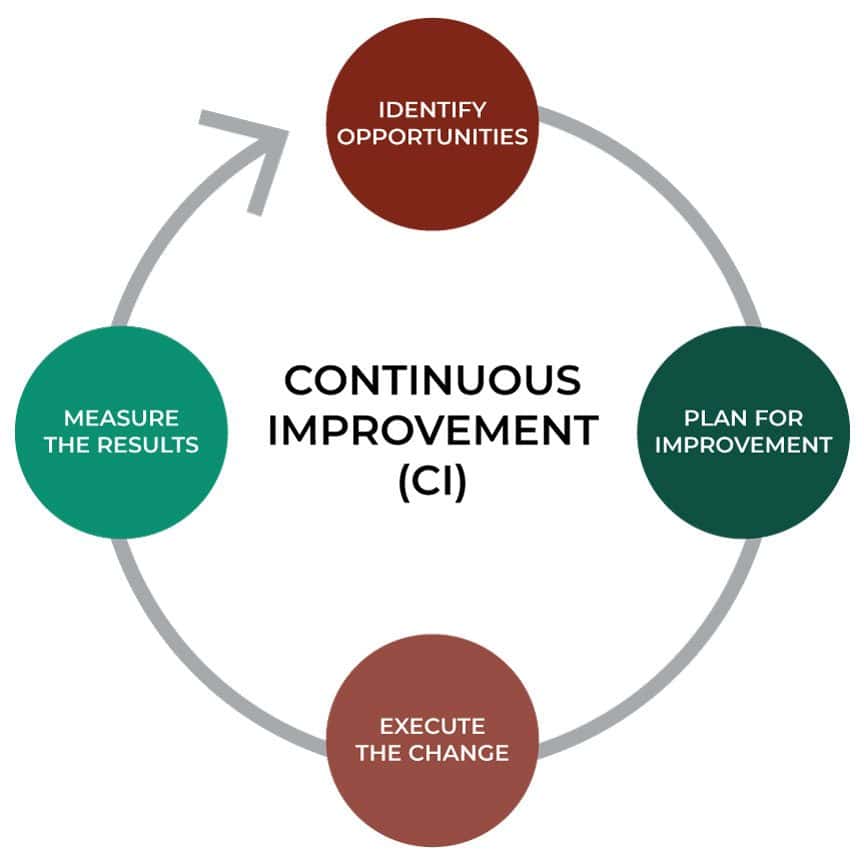
持續改善是指為改善組織內部的流程、產品或服務而進行的系統性、持續性工作。這種理念秉持著「改進的空間永無止境」的理念,並力求透過循序漸進的變革來實現卓越。
持續改善的核心包括:
- 識別機會: 認識到可以改進的領域,無論是工作流程效率、產品品質或客戶滿意度。
- 做出改變: 實施小規模、漸進式的變革,而不是等待大規模的改革。這些變革通常是基於從組織運作中收集的數據、回饋或見解。
- 衡量影響: 評估變更的效果以確定其成功並了解它們如何有助於整體改進目標。
- 適應與學習: 擁抱學習和適應的文化。 持續改善承認商業環境是動態的,今天有效的方法明天可能需要調整。
持續改善不是一次性項目,而是對卓越的長期承諾。 它可以採取多種形式,例如精益方法論, 六西格瑪 改善實踐,或稱“改善原則”,每一種都提供了一種實現持續改進的結構化方法。最終,它關乎培養一種創新、高效的思維模式,以及對組織業務不斷精益求精的不懈追求。
5 種持續改進方法
以下是各行業廣泛使用的五種持續改善方法:
1/ Kaizen——持續改善方法
Kaizen 持續改善流程(Kaizen,日文意為「改善」)是一個持續改善的過程,以小規模、漸進式的改變為中心。它鼓勵各級員工為改善流程、產品或服務貢獻想法,從而創造一種持續改進的文化。
2/ 精益製造-持續改善方法
精實製造的原則 旨在透過最大限度地減少浪費、確保工作的連續流程並專注於為客戶提供價值來簡化營運。 減少浪費、高效流程和客戶滿意度是此方法的核心。
3/ DMAIC 模型 – 持續改善方法
DMAIC模型 (定義、測量、分析、改進、控制)是六西格瑪方法論中的一種結構化方法。 它涉及:
- 定義: 明確定義問題或改進機會。
- 測量: 量化當前狀態並建立基準指標。
- 分析: 調查問題的根本原因。
- 提高: 實施解決方案和增強功能。
- 控制: 確保改進隨著時間的推移而持續。
4/ 限制理論-持續改進方法
什麼是約束理論? 限制理論 (TOC) 著重於識別和解決系統內最重要的限制因素(限制)。 透過有系統地改善或消除約束,組織可以提高整個系統的整體效率和生產力。
5/ 方針管理-持續改善方法
方針管理規劃是一種源自日本的策略規劃方法。它旨在將組織的目標與日常活動相協調。方針管理透過結構化的流程,確保組織中的每個人都朝著共同的目標努力,從而創造一個具有凝聚力、以目標為導向的工作環境。
持續改進的 8 個基本工具
探索觸手可及的持續改善工具庫,準備完善並提升您的流程。
1/ 價值流圖
價值流圖 是一種涉及創建視覺表示以分析和改進工作流程的工具。 透過規劃從開始到結束的整個流程,組織可以識別低效率、減少浪費並優化工作流程,最終提高整體生產力。
2/ 現場漫步
什麼是現場行走? 現場巡視是指前往實際工作場所(或「現場」),觀察、學習並了解流程的真實情況。這種親身實踐的方式使領導者和團隊能夠透過與工作參與者直接接觸,獲得洞見、發現改進機會,並培養持續改進的文化。
3/ PDCA循環(計畫、執行、檢查、行動)
曼徹斯特 PDCA循環 是實現持續改進的重要工具。 它幫助個人和組織透過四個階段來識別問題:
- 計劃: 識別問題並規劃改進。
- 這樣做: 最好先小規模地測試一下這個計劃。
- 檢查: 評估結果並分析數據。
- 法案: 根據結果採取行動,無論是標準化改進、調整計劃或擴大規模。
這個循環過程確保了系統性和迭代的改進方法。
4/ 看板
看板 是一個視覺化管理系統,有助於有效管理工作流程。 它涉及使用卡片或視覺信號來表示在流程的不同階段移動的任務或項目。 看板提供了工作的清晰視覺化表示,減少了瓶頸,並增強了系統內任務的整體流程。
5/ 六西格瑪 DMAIC
曼徹斯特 6西格碼DMAIC 方法論是一種結構化的流程改善方法。為了確保專案順利進行,遵循結構化方法至關重要。
這涉及
- 定義問題和專案目標,
- 量化當前狀態並建立基準指標,
- 調查問題的根本原因,
- 實施解決方案和增強功能,
- 確保改進隨著時間的推移持續下去,並保持一致的品質。
6/根本原因分析
根本原因分析方法 是一種專注於識別和解決問題根本原因而不僅僅是治療症狀的工具。 透過找到問題的根源,組織可以實施更有效、更持久的解決方案,防止問題再次發生並促進持續改善。
搭配簡單的 根本原因分析模板,該工具提供了用於調查問題的有組織的框架。 這有助於組織採取循序漸進的方法來解決問題,並鼓勵持續改善的文化。
7/ 五個為什麼
曼徹斯特 五個為什麼方法 這是一種簡單卻有效的技巧,可以深入探討問題的根源。它需要反覆問“為什麼”(通常五次),直到找到核心問題。這種方法有助於發現導致問題的根本因素,從而促進有針對性的解決方案。
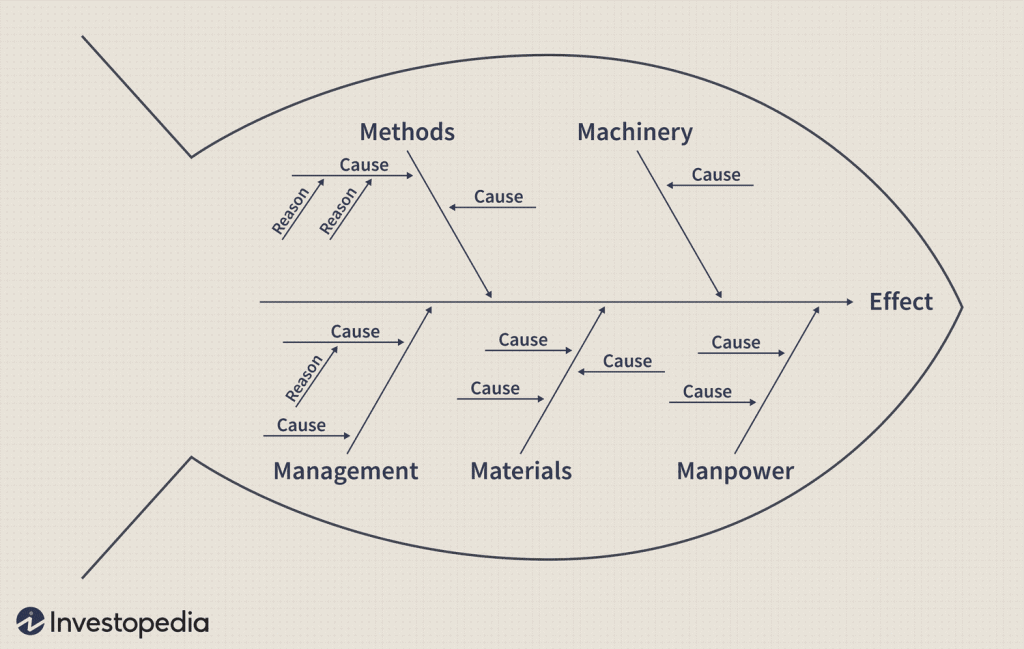
8/ 石川圖
An 石川圖魚骨圖,或稱魚骨圖,是一種用於解決問題的視覺化工具。 它說明了問題的潛在原因,並將其分類為類似魚刺的分支。 這種圖形表示可以幫助團隊識別和探索導致問題的各種因素,從而更容易理解複雜的問題並設計有效的解決方案。
關鍵要點
在總結我們對持續改進方法論的探索後,我們發現了組織進化的關鍵。從Kaizen的細微但影響深遠的變革,到六西格瑪的結構化方法,這些持續改進方法論塑造了持續改進的格局。
當你踏上持續改善之旅時,不要忘記使用 啊哈幻燈片。使用 AhaSlides' 互動功能 以及 可自訂的設計模板,AhaSlides 已成為培養持續改善文化的寶貴工具。無論是促進腦力激盪會議、繪製價值流圖,還是進行根本原因分析,AhaSlides 都能提供一個平台,讓您的持續改進計劃不僅有效,而且引人入勝。
常見問題
持續改善的四個階段是什麼?
持續改善的 4 個階段:辨識問題、分析現況、制定解決方案。 以及實施和監控
六西格瑪持續改善方法是什麼?
六西格瑪持續改善方法:
- DMAIC(定義、測量、分析、改善、控制)
- DMADV(定義、測量、分析、設計、驗證)
持續改進的模式有哪些?
持續改善模型:PDCA(計劃、執行、檢查、行動)、約束理論、方針管理計劃。







