In einem stressigen und hektischen Umfeld ist es hilfreich, sich bei Entscheidungen mehr als einmal auf sein Bauchgefühl zu verlassen.
Aber zu wissen, wann Sie Ihre anwenden müssen intuitives Denken ist schwierig. Wenn Sie verstehen, was es ist und wie Sie es zum Laufen bringen können, können Sie großartige Entscheidungen mit guten Ergebnissen treffen.
Tauchen Sie ein, um weitere Einblicke zu erhalten👇
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Was ist intuitives Denken?
- Was sind die 4 Arten des intuitiven Denkens?
- Sind intuitive Gedanken gut oder schlecht?
- Tipps, um ein intuitiverer Denker zu werden
- Fazit
- Häufig gestellte Fragen
Weitere Tipps zur Entwicklung von Soft Skills
| Was ist das Gegenteil von intuitivem Denken? | Kontraintuitiv |
| Wer hat den Begriff „intuitives Denken“ erfunden? | Henri Bergson |
| Wann warBegriff „Intuitives Denken“ gefunden? | 1927 |

Auf der Suche nach einem besseren Engagement-Tool?
Sorgen Sie für noch mehr Spaß mit den besten Live-Umfragen, Quizzen und Spielen, die alle in AhaSlides-Präsentationen verfügbar sind und direkt mit Ihrem Publikum geteilt werden können!
🚀 Kostenlos anmelden☁️
Was ist intuitives Denken?

Stellen Sie sich vor, Sie sind ein professioneller Baseballspieler und stehen an der Home Plate. Der Pitcher holt aus und wirft einen Fastball direkt auf Sie. Sie haben nur den Bruchteil einer Sekunde Zeit zu reagieren – für bewusstes Nachdenken bleibt keine Zeit!
Doch dann passiert etwas Erstaunliches – Ihr Körper weiß, was zu tun ist. Ohne nachzudenken, schwingen Ihre Hände in Position und knacken! Sie landen einen perfekten Treffer.
Woher kam diese Einsicht? Deine Intuition.
Tief im Inneren hat ein Teil Ihres Gehirns subtile Hinweise wie die Bewegung des Werfers, den Spin des Balls usw. erkannt und wusste aufgrund von Tausenden von Wiederholungen im Training und in vergangenen Spielen genau, wie er reagieren sollte.
Das ist intuitives Denken in Aktion. Es ermöglicht uns, nahezu augenblicklich auf wertvolle Erfahrungen zurückzugreifen und Entscheidungen aus dem Bauch heraus zu treffen, ohne bewusste Logik.
Zum Beispiel, wie Cruise in Top Gun einfach die richtigen Bewegungen im Luftkampf spürt oder Neo den Matrix-Code sieht, ohne ihn zu verstehen.
Und das Beste daran? Intuition ist nicht nur für Reaktionen da – sie ist auch eine Superkraft für Erkenntnisse und Schöpfung.
Diese „Aha!“-Momente des Verstehens oder innovativer Lösungen sprudeln oft aus unserer Intuition, bevor die Logik sie vollständig erklären kann.
Was sind die 4 Arten des intuitiven Denkens?
Intuitives Denken wird im Allgemeinen in vier Arten eingeteilt, jede mit unterschiedlichen Merkmalen. Welcher Typ intuitiver Denker bist du?🤔
Kognitive Intuition
Dabei geht es darum, auf die Muster und Schlussfolgerungen zuzugreifen, die wir unbewusst durch Erfahrungen mit kognitiven Herausforderungen gelernt haben.
Es ermöglicht einen schnellen Schemaabgleich und Beurteilungen. Beispiele hierfür sind das sofortige Erkennen von Grammatikmustern, das Lösen komplexer Probleme, das intuitive Erkennen der Antwort auf ein mathematisches Problem auf der Grundlage vertrauter Muster oder die Bewertung von Risiko/Vertrauenswürdigkeit.
Affektive Intuition

Auch Bauchgefühl genannt. Dieser Typ verlässt sich mehr auf Emotionen und Gefühle, um seine Intuitionen zu leiten.
Ohne bewusste Überlegung können sich Dinge richtig anfühlen oder uns unwohl fühlen. Emotionen spielen beispielsweise bei zwischenmenschlichen Urteilen, der Erkennung von Täuschungen und ethisch-moralischen Entscheidungen eine Rolle.
Analytische Intuition

Entwickelt sich aus umfassendem bewussten und automatischen Lernen über Jahre hinweg in einer Fertigkeit oder einem Bereich.
Experten können komplexe Situationen intuitiv interpretieren und angemessen reagieren. Beispiele hierfür sind Meisterschachspieler, erfahrene Ärzte und andere Fachleute mit umfassender Erfahrung auf ihrem Gebiet.
Verkörperte Intuition

Verlässt sich auf muskuläres, propriozeptives und sensorisches Lernen.
Entwickelt sich durch körperliche Übung und bewegungsbasierte soziale Erfahrungen. Dinge wie Koordinationsfähigkeiten, Gleichgewicht, Interpretation nonverbaler emotionaler/sozialer Signale durch Gesichtsausdruck, Körpersprache usw. fallen in diese Kategorie.
Einige umfassen auch:
- Soziale Intuition – Bezeichnet die Fähigkeit, soziale Dynamiken, Normen und Interaktionen intuitiv und ohne bewusste Überlegung zu verstehen. Sie beeinflusst unter anderem die Interpretation von Emotionen, die Vorhersage von Verhalten, das Erkennen von Beziehungen und Machtstrukturen sowie das Erfassen von Gruppeneinflüssen/-dynamiken.
- Generative Intuition – Neue Ideen und Innovationen hervorbringen oder Probleme auf neuartige Weise erkennen, indem verschiedene Arten von Informationen intuitiv kombiniert werden. Beispiele hierfür sind Erfindungen, innovatives Design, bahnbrechende wissenschaftliche Theorien und unerwartete Perspektiven in den Geisteswissenschaften.
Alle vier Typen liefern schnelle Erkenntnisse, die bewusst langsamer erschlossen werden können. Und sie interagieren oft – kognitive Muster können affektive Reaktionen auslösen, die das Erfahrungslernen langfristig beeinflussen. Die effektive Entwicklung jeglicher Art von Intuition beruht darauf, sich kontinuierlich neuen Erfahrungen und reflektiertem Lernen auszusetzen.
Sind intuitive Gedanken gut oder schlecht?
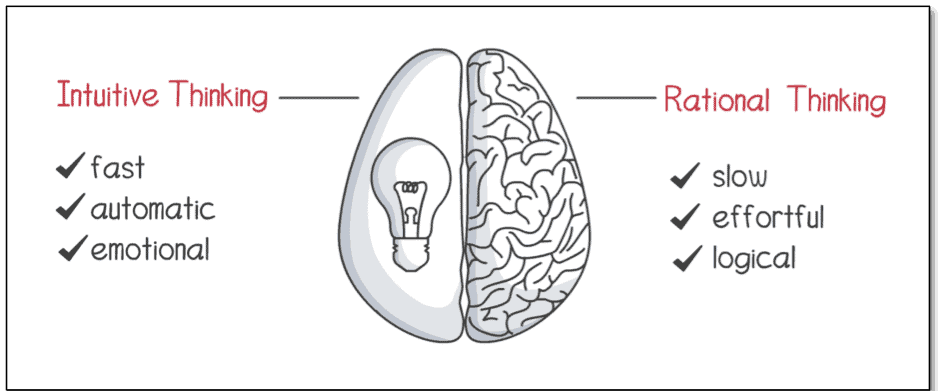
Intuitives Denken ist ein zweischneidiges Schwert. Es kann von großem Nutzen sein, wenn das Fachwissen durch umfassende Erfahrung aufgebaut wurde, aber gefährlich, wenn man sich bei Entscheidungen mit hohem Risiko darauf verlässt und es an einer Faktenbasis mangelt.
Zu den potenziellen Vorteilen des intuitiven Denkens gehören:
- Geschwindigkeit – Intuition ermöglicht sehr schnelle Entscheidungsfindung wenn die Zeit begrenzt ist. Dies kann von Vorteil sein.
- Auf Erfahrungen basierende Erkenntnisse – Intuition bezieht die unbewussten Lehren aus Erfahrungen ein, die nützliche Perspektiven bieten können.
- Kreativität – Intuition kann neue Verbindungen und innovative, unkonventionelle Ideen ermöglichen.
- Erste Ahnungen – Intuitive Bauchgefühle können als Ausgangspunkt für weitere Erkundungen und Bestätigungen dienen.
Zu den möglichen Nachteilen des intuitiven Denkens gehören:
- Voreingenommenheit – Intuition ist anfällig für kognitive Voreingenommenheit wie Ankereffekte, Affektheuristik und Bevorzugung innerhalb der Gruppe, die Urteile verzerren.
- Ungültige Muster – Intuitive Muster können auf veralteten, falschen oder einmaligen Erfahrungen aus der Vergangenheit und nicht auf stichhaltigen Beweisen beruhen.
- Rechtfertigung – Es besteht ein Instinkt, intuitive Gedanken zu rechtfertigen, anstatt ihre Richtigkeit unvoreingenommen zu untersuchen.
- Holismus statt Detail – Die Intuition konzentriert sich auf umfassendere Themen, statt wichtige Feinheiten sorgfältig zu analysieren.
- Selbstgefälligkeit – Die Intuition kann gründliches, wohlüberlegtes Denken verhindern und stattdessen dazu verleiten, sich auf das Gefühl zu verlassen.
Tipps, um ein intuitiverer Denker zu werden

Hier sind einige Tipps, wie Sie intuitiver denken können. Mit der Zeit stärken diese Strategien Ihr intuitives Denken durch vielfältiges, reflektiertes Aussetzen und flexibles Denken:
- Sammeln Sie umfassende praktische Erfahrung in Ihrem Fachgebiet. Intuition entsteht durch das unbewusste Erkennen von Mustern in Ihren Erfahrungen. Fordern Sie sich immer wieder selbst heraus.
- Übe Achtsamkeit und Selbstwahrnehmung. Achte auf dein Bauchgefühl und deine Ahnungen, ohne zu urteilen. Mit der Zeit wirst du lernen, deiner Intuition mehr zu vertrauen.
- Divergentes Denken fördern. Stellen Sie Assoziationen zwischen nicht zusammenhängenden Konzepten her. Brainstormen Sie umfassend. Intuition kombiniert Ideen auf neue Weise.
- Machen Sie während der Problemlösung Pausen. Durch die Inkubation können Intuitionen aus Ihrem Unterbewusstsein an die Oberfläche gelangen. Gehen Sie spazieren und lassen Sie die Seele baumeln.
- Entwickeln Sie Metakognition. Analysieren Sie vergangene Intuitionen – was war richtig und warum? Bauen Sie Selbsterkenntnis über Ihre intuitiven Stärken auf.
- Achten Sie auf Ihre Träume/Tagträume. Diese können intuitive Erkenntnisse außerhalb logischer Normen liefern.
- Studieren Sie Bereiche, die sich von Ihrem Fachwissen unterscheiden. Neuartige Informationen fördern Ihre intuitiven Assoziationen und Problemlösungsperspektiven.
- Vermeiden Sie eine Abweisung aus dem Bauch heraus. Geben Sie Ihren Ahnungen eine Chance, indem Sie sie genauer prüfen, bevor Sie sie verwerfen.
Fazit
Intuitives Denken basiert auf schneller, unbewusster Mustererkennung, Emotionen und Erfahrung statt auf schrittweisem Denken. Mit etwas Übung können wir unsere Intuition trainieren, sodass sie fast wie ein sechster Sinn funktioniert – und uns in jeder Situation zu hervorragenden Problemlösern macht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Was machen intuitive Denker?
Intuitive Denker verlassen sich in erster Linie auf ihr Bauchgefühl, durch Erfahrung erkannte implizite Muster und die Fähigkeit, unterschiedliche Ideen intuitiv zu verbinden, statt auf eine strenge logische Analyse, wenn sie an Probleme herangehen, Entscheidungen treffen und sich äußern.
Was ist ein Beispiel für intuitives Denken?
Ein Beispiel für intuitives Denken: Ein Schachgroßmeister erkennt sofort den besten nächsten Zug, ohne alle Möglichkeiten bewusst zu analysieren. Seine Intuition basiert auf großer Erfahrung. Oder ein erfahrener Arzt erkennt die Ursache unbekannter Symptome bei einem Patienten anhand subtiler Hinweise und „spürt“, dass etwas nicht stimmt, auch wenn die Testergebnisse es noch nicht erklären.
Ist es besser, logisch oder intuitiv zu sein?
Es gibt keine einfache Antwort auf die Frage, ob es grundsätzlich besser ist, logisch oder intuitiv vorzugehen – beide Ansätze haben Stärken und Schwächen. Die Idee besteht im Allgemeinen darin, beide Ansätze zu vereinen.








