W stresującej i szybko zmieniającej się sytuacji, warto polegać na swojej intuicji przy podejmowaniu decyzji, i to nie tylko raz.
Ale wiedząc, kiedy zastosować swoje intuicyjne myślenie jest trudne. Zrozumienie, co to jest i jak możesz sprawić, by działało, pozwoli ci podejmować świetne decyzje, które przyniosą dobre rezultaty.
Zanurz się, aby uzyskać więcej informacji👇
Spis treści
- Czym jest myślenie intuicyjne?
- Jakie są 4 rodzaje intuicyjnego myślenia?
- Czy myśli intuicyjne są dobre czy złe?
- Wskazówki, jak stać się bardziej intuicyjnym myślicielem
- Podsumowanie
- Najczęściej zadawane pytania
Więcej wskazówek dotyczących rozwijania umiejętności miękkich
| Jakie jest przeciwieństwo myślenia intuicyjnego? | Przeciwny |
| Kto wymyślił termin „myślenie intuicyjne”? | Henri Bergson |
| Kiedy byłznaleziono termin „Myślenie intuicyjne”? | 1927 |

Szukasz lepszego narzędzia do zaangażowania?
Dodaj więcej zabawy dzięki najlepszym ankietom na żywo, quizom i grom, dostępnym w prezentacjach AhaSlides i gotowym do udostępnienia publiczności!
🚀 Zarejestruj się za darmo☁️
Czym jest myślenie intuicyjne?

Wyobraź sobie, że jesteś profesjonalnym baseballistą stojącym przy domowej płycie. Miotacz nakręca się i rzuca piłkę prosto w ciebie. Masz ułamek sekundy na reakcję – nie ma czasu na świadome myślenie!
Ale dzieje się coś niesamowitego – twoje ciało wie, co robić. Bez żadnego uzasadnienia twoje ręce ustawiają się w odpowiedniej pozycji i trzaskają! Uzyskujesz idealne uderzenie.
Skąd to spostrzeżenie? Twoja intuicja.
Głęboko w środku jakaś część twojego mózgu rozpoznawała subtelne wskazówki, takie jak ruch miotacza, rotację piłki itp. i wiedziała dokładnie, jak zareagować, opierając się na tysiącach powtórzeń na treningach i w poprzednich meczach.
To jest intuicyjne myślenie w działaniu. Pozwala nam niemal natychmiast czerpać z bogatych doświadczeń i podejmować „intuicyjne decyzje” bez żadnej świadomej logiki.
Podobnie jak Cruise w Top Gun po prostu wyczuwa właściwe ruchy w walce powietrznej lub Neo widzi kod Matrix bez zrozumienia.
Najlepsza część? Intuicja nie służy tylko do reakcji – to także supermoc do wglądu i tworzenia.
Te momenty „aha!” zrozumienia lub innowacyjnych rozwiązań często rodzą się w naszej intuicji, zanim logika zdąży je w pełni wyjaśnić.
Jakie są 4 rodzaje intuicyjnego myślenia?
Myślenie intuicyjne dzieli się ogólnie na 4 rodzaje, każdy o odmiennych cechach. Jakim typem intuicyjnego myśliciela jesteś?🤔
Intuicja poznawcza
Polega ona na dostępie do wzorców i wniosków, których nieświadomie nauczyliśmy się poprzez doświadczenia związane z wyzwaniami poznawczymi.
Pozwala na szybkie dopasowywanie schematów i ocenę. Przykłady obejmują natychmiastowe rozpoznawanie wzorców gramatycznych, rozwiązywanie złożonych problemów, intuicyjne szukanie odpowiedzi na zadanie matematyczne w oparciu o znane wzorce lub ocenę ryzyka/wiarygodności.
Intuicja afektywna

Nazywane także uczuciami jelitowymi. Ten typ opiera się bardziej na emocjach i uczuciach, aby kierować intuicją.
Rzeczy mogą wydawać się właściwe lub sprawiać, że czujemy się nieswojo bez świadomego rozumowania. Jest to zaangażowane w takie rzeczy jak osądy interpersonalne, wykrywanie oszustw i podejmowanie decyzji etycznych/moralnych, w których emocje odgrywają rolę.
Intuicja analityczna

Rozwija się na podstawie rozległego, przemyślanego i automatycznego uczenia się przez lata w zakresie umiejętności lub domeny.
Eksperci potrafią intuicyjnie interpretować złożone sytuacje i odpowiednio reagować. Przykładami są mistrzowie szachów, eksperci lekarze i inni profesjonaliści z głębokim doświadczeniem w swojej dziedzinie.
Ucieleśniona intuicja

Opiera się na uczeniu się mięśniowym, proprioceptywnym i sensorycznym.
Rozwija się poprzez praktykę fizyczną i doświadczenia społeczne oparte na ruchu. Rzeczy takie jak umiejętności koordynacji, równowaga, interpretowanie niewerbalnych sygnałów emocjonalnych/społecznych poprzez wyraz twarzy, język ciała itp. należą do tej kategorii.
Niektóre obejmują również:
- Intuicja społeczna – odnosi się do zdolności intuicyjnego rozumienia dynamiki społecznej, norm i interakcji bez świadomego rozumowania. Obszary, na które wpływa, obejmują interpretowanie emocji, przewidywanie zachowań, rozróżnianie relacji i struktur władzy oraz wyczuwanie wpływów/dynamiki grupy.
- Intuicja generatywna – pobudzanie nowych pomysłów, innowacji lub widzenie problemów w nowatorski sposób poprzez intuicyjną syntezę różnych typów informacji. Przykłady obejmują wynalazek, innowacyjny projekt, przełomowe teorie naukowe i nieoczekiwane perspektywy w sztuce/naukach humanistycznych.
Wszystkie cztery typy dostarczają szybkich spostrzeżeń, do których dostęp świadomy może być wolniejszy. I często oddziałują na siebie – wzorce poznawcze mogą wyzwalać reakcje afektywne, które wpływają na uczenie się przez doświadczenie w dłuższej perspektywie. Skuteczne rozwijanie każdego typu intuicji polega na ciągłym wystawianiu się na nowe doświadczenia i refleksyjnym uczeniu się.
Czy myśli intuicyjne są dobre czy złe?
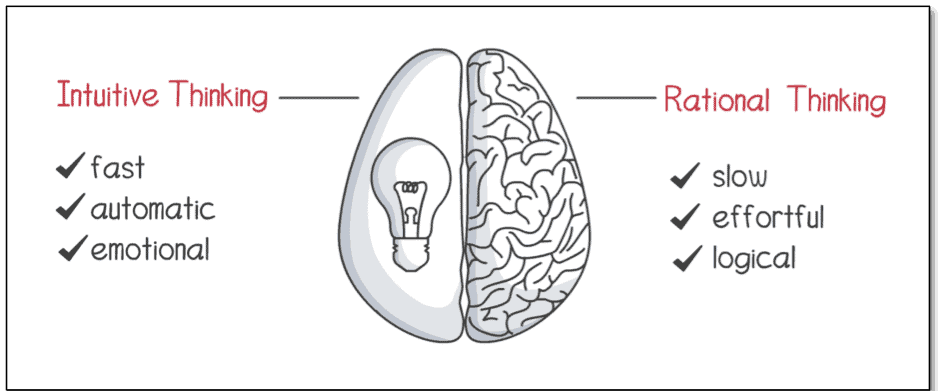
Intuicyjne myślenie to miecz obosieczny. Może być bardzo korzystna, gdy specjalistyczną wiedzę zbudowano na podstawie rozległego doświadczenia, ale niebezpieczna, gdy polega się na niej w przypadku podejmowania decyzji o wysokiej stawce, nieposiadających podstawy dowodowej.
Potencjalne korzyści płynące z myślenia intuicyjnego obejmują:
- Prędkość – Intuicja pozwala na bardzo szybkie podejmowanie decyzji kiedy czas jest ograniczony. To może być korzystne.
- Wnioski oparte na doświadczeniu – intuicja uwzględnia nieświadome lekcje płynące z doświadczenia, które mogą dostarczyć użytecznych perspektyw.
- Kreatywność – Intuicja może ułatwiać nawiązywanie nowych kontaktów i powstawanie innowacyjnych, nieszablonowych pomysłów.
- Początkowe przeczucia – Intuicyjne przeczucia mogą stanowić punkt wyjścia do dalszych badań i weryfikacji.
Potencjalne wady myślenia intuicyjnego obejmują:
- Błędy – intuicja jest podatna na błędy poznawcze, takie jak zakotwiczenie, heurystyka afektywna i faworyzowanie grupy wewnętrznej, które wypaczają osądy.
- Nieprawidłowe wzorce – intuicyjne wzorce mogą opierać się na przestarzałych, nieprawidłowych lub jednorazowych doświadczeniach z przeszłości, a nie na solidnych dowodach.
- Uzasadnienie – istnieje instynkt uzasadniania intuicyjnych myśli, zamiast bezstronnego badania ich dokładności.
- Holizm ponad szczegółami – intuicja koncentruje się na szerszych tematach, zamiast starannie analizować ważne subtelności.
- Zadowolenie – Intuicja może zniechęcić do gruntownego, przemyślanego rozumowania na rzecz kierowania się uczuciami.
Wskazówki, jak stać się bardziej intuicyjnym myślicielem

Oto kilka wskazówek, jak stać się bardziej intuicyjnym myślicielem. Z biegiem czasu strategie te wzmacniają Twoje intuicyjne myślenie poprzez różnorodną, refleksyjną ekspozycję i elastyczne myślenie:
- Zdobądź rozległe doświadczenie praktyczne w swojej dziedzinie. Intuicja pochodzi z nieświadomego rozpoznawania wzorców w tym, na co zostałeś wystawiony. Ciągle rzucaj sobie wyzwania.
- Praktykuj uważność i samoświadomość. Zauważaj swoje przeczucia i przeczucia bez osądzania. Z czasem nauczysz się bardziej ufać swojej intuicji.
- Zachęcaj do odmiennego myślenia. Twórz skojarzenia między niepowiązanymi pojęciami. Szeroko przeprowadź burzę mózgów. Intuicja łączy pomysły w nowy sposób.
- Rób przerwy podczas rozwiązywania problemów. Inkubacja pozwala intuicji wypłynąć na powierzchnię z podświadomości. Idź na spacer i pozwól swoim myślom wędrować.
- Rozwijaj metapoznanie. Analizuj przeszłe intuicje – co było trafne i dlaczego? Buduj samoświadomość swoich intuicyjnych mocnych stron.
- Zwróć uwagę na swoje sny/marzenia. Mogą one zapewnić intuicyjny wgląd poza normami logicznymi.
- Studiuj domeny inne niż Twoja specjalizacja. Nowatorskie informacje napędzają Twoje intuicyjne skojarzenia i sposoby rozwiązywania problemów.
- Unikaj odrzucenia reakcji jelit. Daj przeczuciom szansę na dalsze zbadanie, zanim je odrzucisz.
Podsumowanie
Intuicyjne myślenie opiera się na szybkim, podświadomym rozpoznawaniu wzorców, emocjach i doświadczeniu, a nie na rozumowaniu krok po kroku. Dzięki praktyce możemy wytrenować naszą intuicję, aby działała niemal jak szósty zmysł – czyniąc nas niesamowitymi rozwiązywaczami problemów w każdym scenariuszu.
Najczęściej zadawane pytania
Co robią osoby myślące intuicyjnie?
Osoby myślące intuicyjnie polegają przede wszystkim na swoich przeczuciach, ukrytych wzorcach rozpoznanych na podstawie doświadczenia i umiejętności intuicyjnego łączenia odmiennych pomysłów, a nie na ścisłej analizie logicznej podczas podejścia do problemów, podejmowania decyzji i wyrażania siebie.
Jaki jest przykład myślenia intuicyjnego?
Przykładem ilustrującym myślenie intuicyjne jest: arcymistrz szachowy natychmiast rozpoznający najlepszy następny ruch bez świadomej analizy wszystkich możliwości. Jego intuicja opiera się na ogromnym doświadczeniu lub doświadczony lekarz wykrywający przyczynę nieznanych objawów u pacjenta na podstawie subtelnych wskazówek i „czucia”, że coś jest nie tak, nawet jeśli wyniki testów jeszcze tego nie wyjaśniają.
Lepiej kierować się logiką czy intuicją?
Nie ma prostej odpowiedzi na pytanie, czy z natury lepiej jest być logicznym czy intuicyjnym – oba podejścia mają swoje mocne i słabe strony. Pomysł ten jest ogólnie uważany za równowagę obu podejść.








